Looking at ESG in Crypto, Blockchain, and Public Equities
Investors can face risks related to noncompliance with respect to tightening regulations targeting the crypto market. This market also faces challenges related to the energy intensity of crypto mining which can have a large carbon footprint, depending on the sources of energy used in mining. On the other hand, the efficiency of crypto blockchains may have positive social impacts, such as reducing the costs of transactions for people sending remittances. Moreover, some cryptos function without relying on mining operations by using a proof-of-stake rather than proof-of-work consensus mechanism.
Features of blockchain that may support use cases across multiple industries

Beyond the volatile crypto market, blockchain has several features that lend well to commercial applications. Blockchain can help improve the transparency, speed and efficiency of data transfers and monetary transactions. Businesses in multiple industries are using blockchain tools to enhance payment platforms and secure supply chain management systems.
Sustainalytics’ latest Thematic Research report, An ESG Lens on Blockchain and Public Equities, surveys environmental, social and governance (ESG) risks and opportunities related to applications of blockchain technology that are being developed by listed companies across multiple sectors of the economy.
Report Structure
The report has three main parts. The first section provides a primer on blockchain, crypto and related ESG issues. The second section focuses on a sample of 10 blockchain themed exchange traded funds (ETFs). The third section assesses companies on relevant ESG criteria and compares a selection of industry peers developing blockchain tools.
ETF analysis
Discussions about ESG issues linked to blockchain have tended to focus on crypto, but other aspects of this technology present different risks and opportunities. To identify ESG issues related to blockchain applications in the public equities market, our analysis starts by looking at 10 blockchain-themed ETFs.
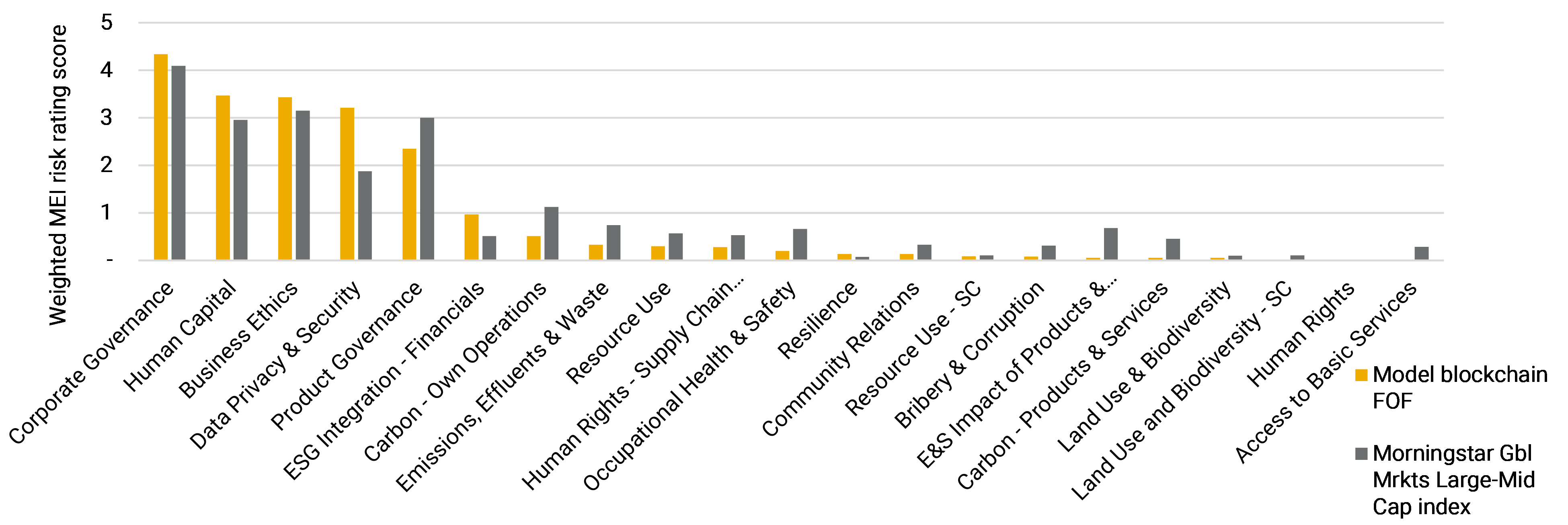
We combine 144 constituents of these ETFs that are covered by our comprehensive ESG Risk Ratings into a model fund of funds (FOF) and assess its ESG characteristics relative to the Morningstar Global Markets (Gbl Mrkts) Large-Mid index.
As shown in the chart below, we find that our model FOF faces higher levels of unmanaged risk in areas that are critical for companies developing blockchain applications. Compared to the index, the weighted risk scores of the model FOF are 9% higher on Business Ethics, 17% higher Human Capital and 71% higher in Data Privacy and Security. We attribute the outsized unmanaged risk of the FOF on these issues to its high concentration of companies in the Information Technology and Financials sectors, which face high levels of exposure to the issues. These Material ESG Issues (MEIs) may constitute an area of interest for investors in this space to assess and engage with companies.
Material ESG Issue risks, blockchain model FOF vs Morningstar Global Markets Large-Mid Cap index
Industry analysis
Our analysis of blockchain applications in different sectors identifies four key areas of research that investors in this space can integrate into their portfolio, engagement, and financing strategies.

1. Financials companies sampled from our model blockchain FOF tend to face high levels of unmanaged risk on two MEIs: Product Governance and Business Ethics
2. Human Capital and Data Privacy and Security are critical MEIs for companies developing blockchain tools to support business activities across multiple sectors. Companies in the Conglomerates and Software and Services industries are highly exposed to these issues because they face a growing demand for blockchain developers and heightened cybersecurity risks related to data breaches and hacks.
3. Resource-intensive industries are developing blockchain applications to address environmental risks. Companies in the Utilities, Mining and Semiconductor industries are at the early stages of developing blockchain tools to address environmental risks related to resource use.
4. Early blockchain adopters in the Consumer Goods sector are integrating blockchain into data management systems with the aim of improving issues related to supply chain management. Companies in the Household and Personal Products (HPP) industry are using blockchain systems to address supply chain management issues and secure payment processing. Major Food Retail companies have been experimenting with blockchain to improve supply chain transparency and traceability for selected food products.
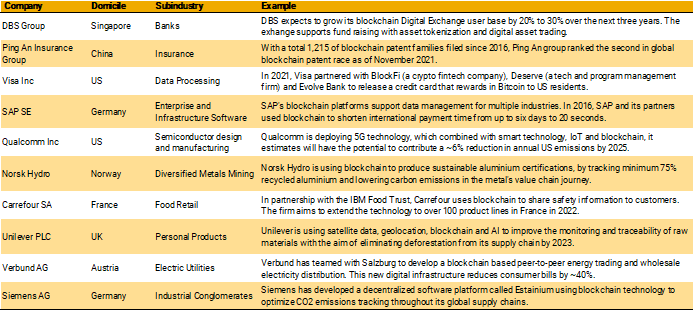
Looking at case studies related to these themes, we identify industry leaders across markets in Asia, North America and Europe. The 10 companies listed in the table below are at the forefront of innovating with blockchain and have strong management programs in place to mitigate relevant ESG risks.
Leading companies featured in the report
To learn more about these companies and our analysis, download the An ESG Lens on Blockchain and Public Equities full report.